Particle Size Distribution (PSD)
To measures particle size distribution through light scattering technology we have (Blue wave of Micrortac) . The measure range from 10,7 nm up to 2000 µm .
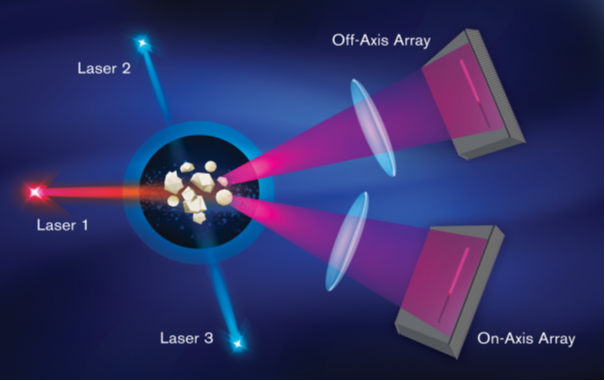
The PDS has tri-laser and allows light scattering measurements to be made from the forward low angle region to almost the entire angular spectrum (0.2 to 165 degrees). It does so by a combination of three lasers and two detector arrays, all in fixed positions. The primary laser (on-axis) produces scatter from nearly on-axis to about 60 degrees, detected by a forward array and a high-angle array, both of which have logarithmic spacing of the detector segments. The second laser (off-axis) is positioned to produce scatter beyond the 60 degree level which is detected using the same detector arrays. The third laser (off-axis) is positioned to produce backscatter, again using the same detector arrays. This technique effectively multiplies the number of sensors that are available for detection of scattered light.

Laser beam interacts with mixture of particle sizes where Light is scattered and Scattered light is collected by a Fourier lens. The Fourier lens focuses the light onto a silicon detector where the detector responds to light by producing a series of voltages. This voltages represent signals that produce a pattern that is a fingerprint. An Algorithm is used to calculate the volume percent as a function of particle size.
Particle size inversely proportional to angle while the Intensity increases with size.
The intensity of scattered light has an inverse relationship to the fourth power of the wavelength of the incident light based on the Rayleigh Scattering Principle:
1 Red and 2 Blue Lasers (not LED or filters). The red Laser diode has wave length of λ= 780 nm with intensity of ( I= 1/λ4 =1/(780)4 = 2.7*10-12) and collects light from 0° to 60° while the blue Laser diode has wave length of λ= 405 0nm has intensity of ( I= 1/λ4 = 1/(405)4 = 3.7*10-11) and collects light from 60° - 80°. The second blue Laser diode collects light from 80° - 165°. A blue laser produces scattered light that is more than 13 times more intense than a red laser. Therefore, the higher intensity makes it easier to detect smaller sized particles with a blue laser! Blue laser is made from Indium Gallium Phosphide – InGaPH.
The Bluewave is fitted with a sample circuit system (Sample Dispersion Controller) with short paths from dispersion unit to measurement cell to optimize sample flow. The speed of the centrifugal pump can be adjusted according to the viscosity properties of the sample. The measure cell that come into contact with the sample are made from resistant quartz glass and all other materials are made from Teflon, stainless steel or Kalrex (chemical compatibility class I). A second integrated pump allows for automatic filling and cleaning.
To calculate of the particle size distribution the Fraunhofer or Mie calculation can be used depends on irregular shape or of spherical particles. This algorithm has been further refined for transparent, absorbing and reflecting particles.