Zeolites as novel adsorbent in water treatment
Research objectives
The objectives of the project are removing organic micropollutants (OMPs) with high-silica zeolites. The aim is to ensure high water quality standards at lower operational costs and at a lower environmental footprint compared to activated carbon.
Project outline
Introduction
Currently, activated carbon filtration is the state-of-the-art for the adsorption of OMPs. Activated carbon can remove a broad range of targeted OMPs. It will also remove non-targeted natural organic matter (NOM). NOM can severely reduce the adsorption capacity for targeted organic pollutants due to adsorption competition, change in adsorbent surface characteristics and pore blockage.
High-silica zeolites can be an attractive alternative adsorbent for activated carbon, as,
- Most NOM molecules are larger than the zeolite pores (<1 nm), and consequently will not compete with targeted OMPs for adsorption.
- The adsorption is more effective with high-silica zeolites than with activated carbon when there is a close match between pollutants’ molecule size and zeolites’ pore size.
- Zeolites can be regenerated in situ with oxidative techniques. This has advantages to the regeneration of activated carbon, which is done off-site by energy-intensive thermal treatment.
Approach
- A broad set of OMPs is selected with variations in molecule charge, size and hydrophobicity. A series of commercial, high-silica zeolites are selected based on a close fit with OMPs in the selected set.
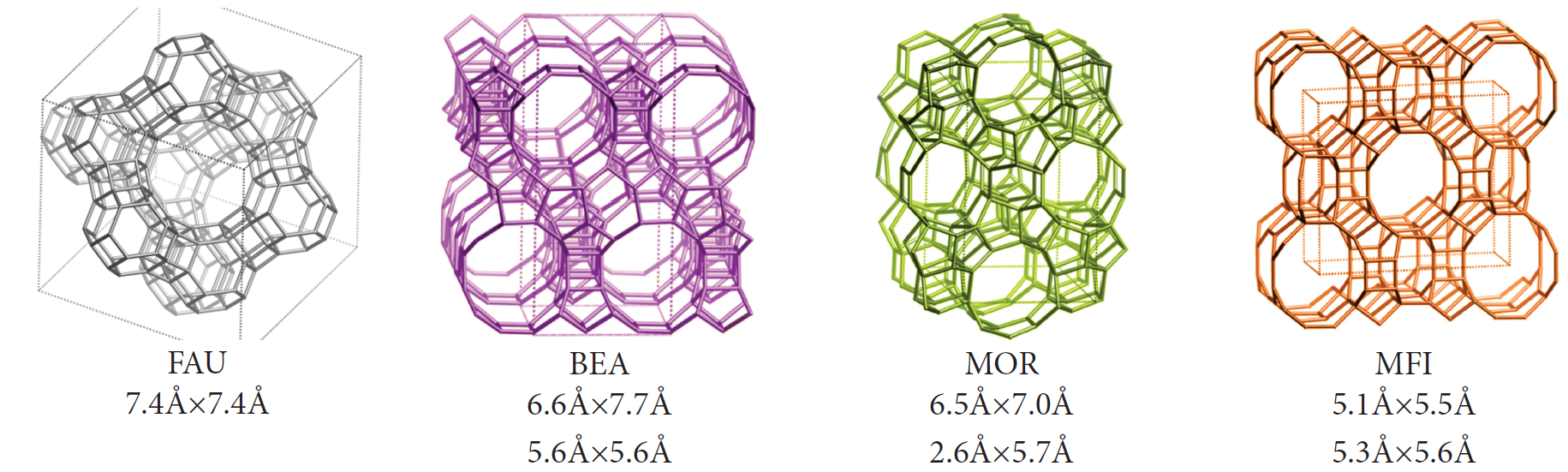
Figure 1 The pore size and structures of four commonly used zeolites.
- With batch experiments with demineralized water with added OMPs on lab scale, equilibrium adsorption of OMPs are measured. Adsorption performance is related to possible adsorption mechanisms (close fit, hydrophobic interaction, charge interaction).
- Different water types are used as water matrix to assess the influence of NOM competition (or the absence thereof due to size exclusion). The NOM composition of the water types is analyzed by size separation and hydrophobicity separation.
- High-silica zeolite pellets can be synthesized by selected high-silica zeolite powders based on the results of batch experiments. The properties of zeolite pellets relating to the adsorption efficiency, e.g. mechanical strength, pore size and volume, will be characterized. The adsorption experiments of zeolite pellets will be performed in column scale.


Figure 2 High-silica zeolite (a) powders and (b) pellets.
Literature
- De Ridder, D.J., Verberk, J.Q.J.C., Heijman, S.G., Amy, G.L. and Van Dijk, J.C., 2012. Zeolites for nitrosamine and pharmaceutical removal from demineralised and surface water: mechanisms and efficacy. Separation and purification technology, 89, pp.71-77.
- Jiang, N., Shang, R., Heijman, S.G. and Rietveld, L.C., 2018. High-silica zeolites for adsorption of organic micro-pollutants in water treatment: A review. Water research.