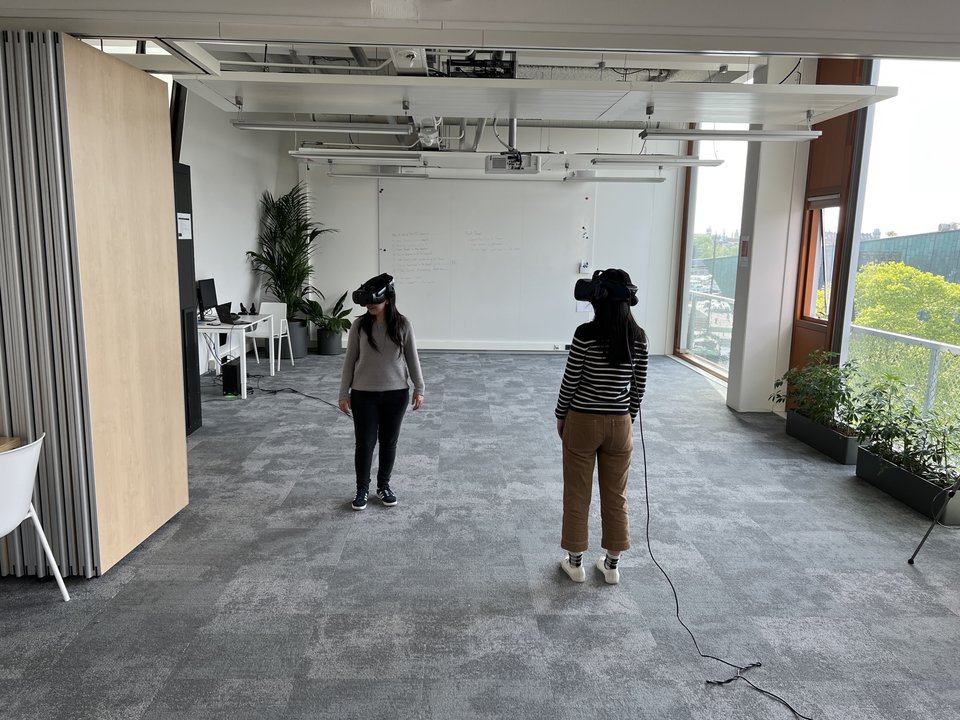
Human mobility behaviour in emergency scenarios

Human mobility behaviour in hypothetical scenarios

Interdisciplinary methodological framework for the adoption of XR for human mobility research

Safe Interaction of pedestrians and cyclists with automated transport (SIPCAT)
Safe Interaction of pedestrians and cyclists with automated transport (SIPCAT) is a project using Virtual Reality to study the interaction among pedestrians, cyclists and automated vehicles. This project uses a 3D VR Digital Twin to safely and efficiently study the interaction of pedestrians and cyclists with automated shuttles and delivery robots.
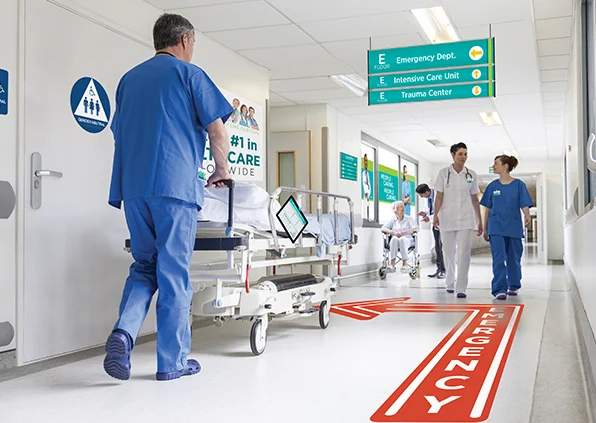
Optimize and evaluate wayfinding design in hospitals by incorporating theories
Extensive research has demonstrated that finding one's way within big buildings structures is often perceived as a complex process for a variety of reasons. In particular, hospitals present a noteworthy context where wayfinding poses a significant challenge for patients, as evidenced by patient complaints reported by hospital management.
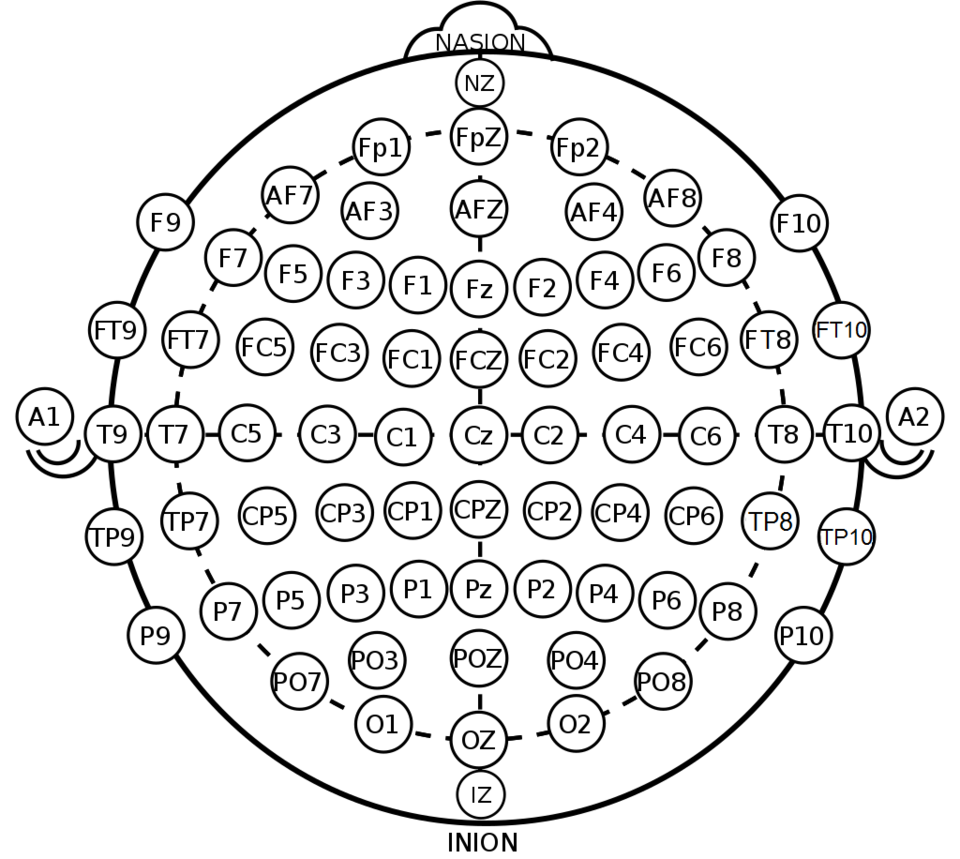
Assessing driver situation awareness and emergency level using EEG signals in traffic scenarios
In response to rising traffic complexities, this study investigates Electroencephalogram(EEG) technology's potential to predict and differentiate accident severity levels in advance by monitoring driver responses in simulated emergencies. The role of driver situation awareness(SA) in this context is also considered, in order to simultaneously study the impact of SA on the driver's ability to differentiate between accident levels.
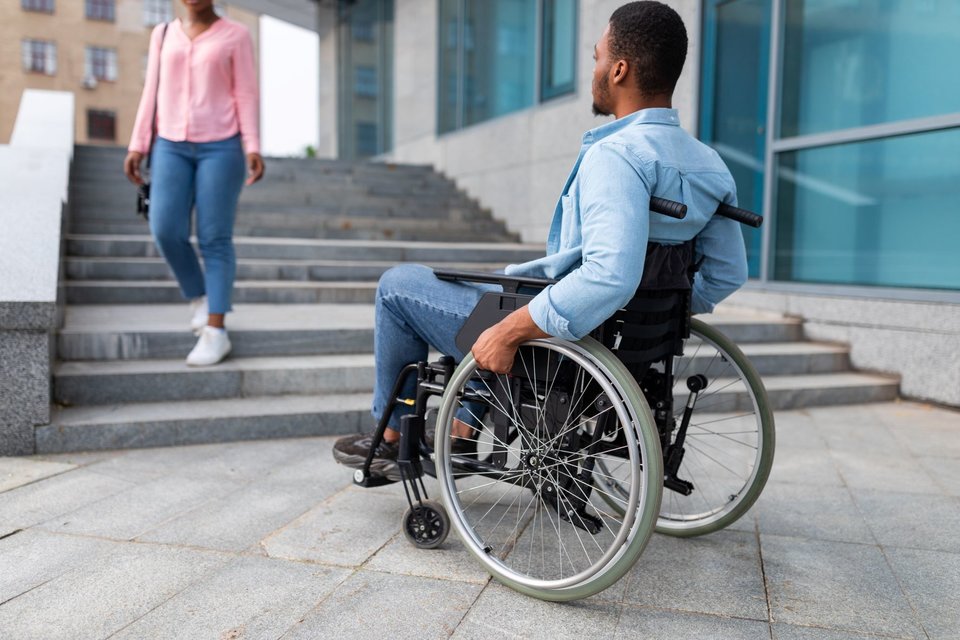
WheelVR: Using Virtual Reality to understand wheelchair pedestrians’ road-crossing behavior
Pedestrians with reduced mobility (PRM) are particularly vulnerable when it comes to road safety. Research on PRM’s interactions with other road users is still lacking. Understanding PRM’s road crossing behavior is crucial for designing accessible, inclusive, and safe mobility systems.
Impact of various IT-based crowd management measures on pedestrian behaviour
This project aims to quantify the impact of various IT-based crowd management measures on pedestrian behaviour, such that those measure can be implemented by operators of crowded pedestrian infrastructures.
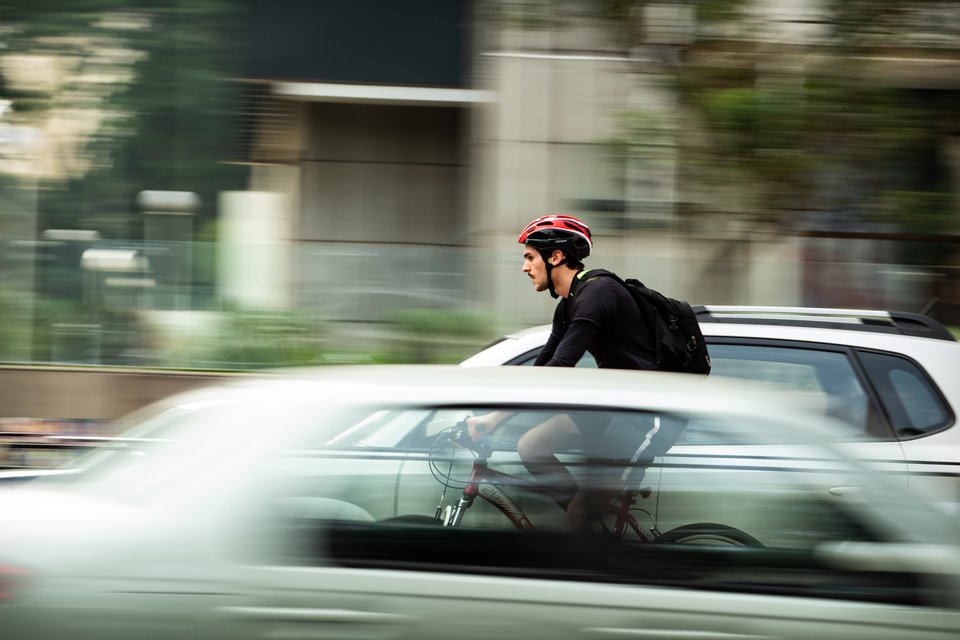
Exploring cyclist-automated vehicle interactions through Virtual Reality
With increasing automation on our roads, understanding cyclist interactions with automated vehicles is essential. Using a cycling simulator, our study delves into the effects of automated vehicles’ capabilities and implicit communication, assessing the impact on cyclists and safety in future automated traffic environments.
Comparison of different XR technologies for pedestrian behavior study
Extended Reality (XR) technologies, such as Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, and Mixed Reality, provide new possibilities for studying pedestrian behavior. Different XR technologies have distinct features regarding immersion, presence, and interaction capabilities. This research project investigates these differences and understands the suitability of different XR technologies for pedestrian behavior study. Novel metrics from the perspective of pedestrian behavior and human-computer interaction will be developed to evaluate the usage of different XR technologies for pedestrian behavior study.