Research
Developing low-carbon, safe and sustainable energy technologies is a necessity in light of a rising world population and urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the impact on climate change. Nuclear energy can play a key role in the energy mix. Six designs of Generation IV nuclear reactors are currently being developed following an international agreement between thirteen member countries (the Generation IV International Forum) -Argentina, Brazil, Canada, France, Japan, the Republic of Korea, South Africa, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, the United States, Euratom, People’s Republic of China, and the Russian Federation- for cooperation in the research and development of future generation of nuclear energy systems. These reactors should be ready for deployment by 2030 to replace the current portfolio of nuclear reactors (mainly second generation Light Water Reactors LWRs) at the end of their operating licenses. These new technologies are not only highly innovative, but also have the potential to provide safer, more reliable and sustainable designs.
One main challenge for their development and commercialisation in the near future is a thorough understanding and modelling of the nuclear fuel physico-chemical properties. Nuclear fuel is at the heart of the energy production process in a reactor. Its performance and safety are first determined by the fuel properties.
Together with a research team of PhDs, Post Docs, master and bachelor students,
- we investigate innovative and ingenious nuclear fuel materials with appealing thermo-physical properties
- we develop new modelling tools to predict fuel physico-chemical properties and performance during reactor operation and accidental scenarios
- we study corrosion chemistry of molten salts towards structural materials in next generation Molten Salt Reactors
- … and many more exciting research fields.
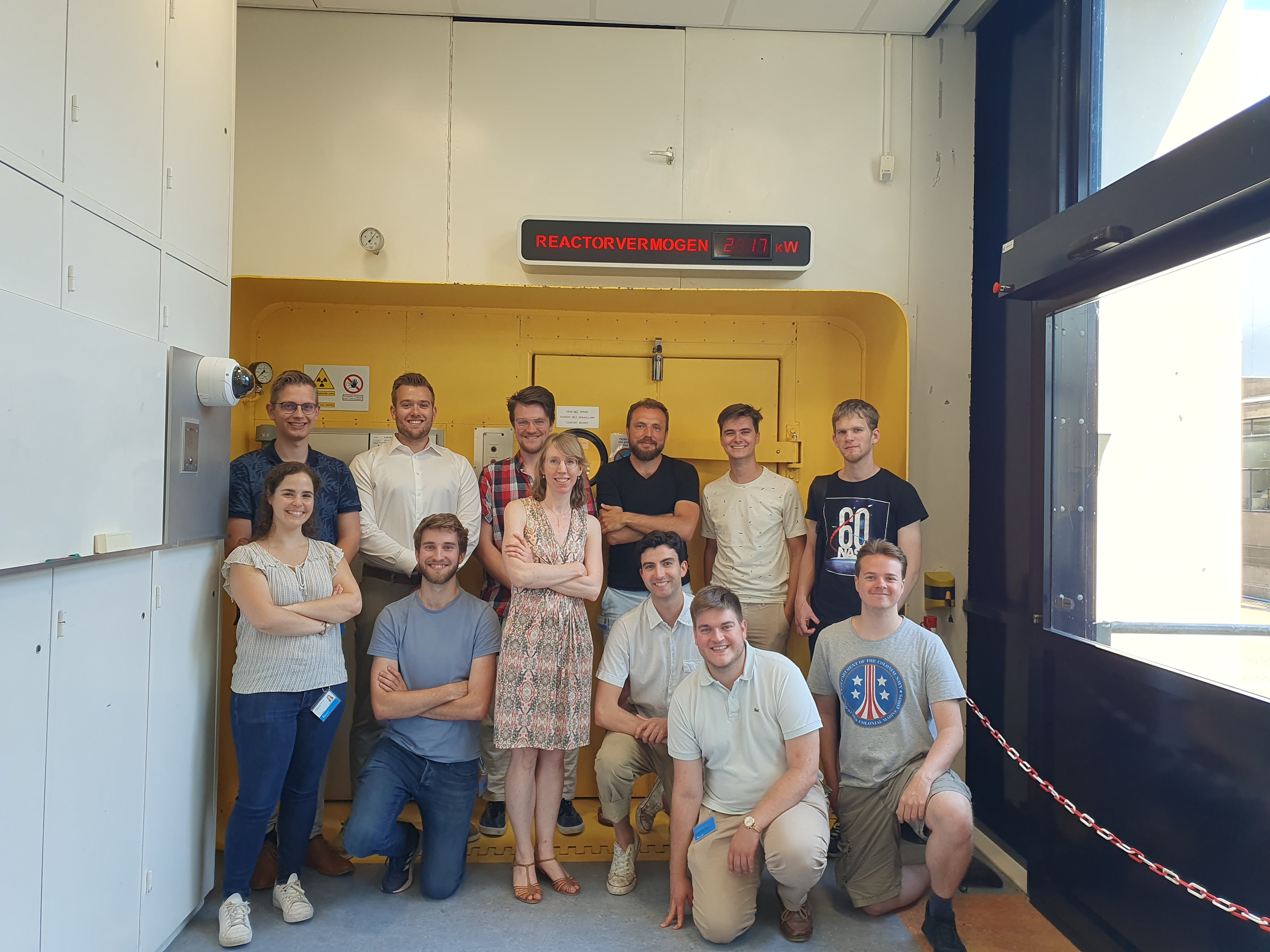

The research team in action