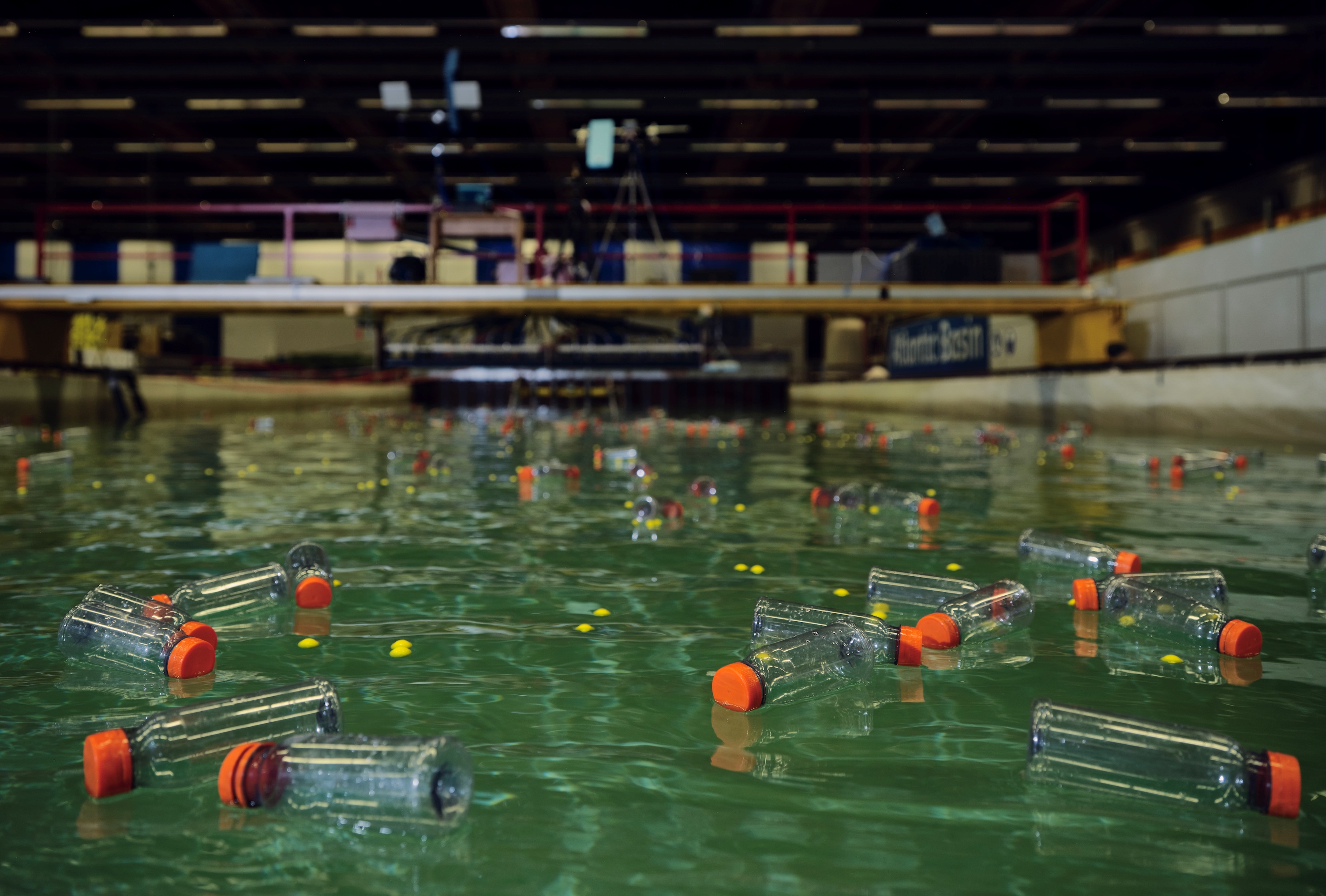Ton van den Bremer
"Understanding how fluids flow is essential to understanding our ocean. Solving numerous challenges for humanity, such as climate change and pollution of marine ecosystems, depends on advances in the field of fluid dynamics."

Ton van den Bremer
Associate Professor Fluid Mechanics, Delft University of Technology
“During the transport of a plastic particle through the ocean, fluid mechanics processes play a role that span many magnitude scales”
Fluid Mechanics of the Ocean Surface
The surface of oceans and seas takes up more than 70% of the total surface of the earth. This surface forms the boundary between two fluids: water and air, ocean and atmosphere. The exchange of gases such as CO2, energy and momentum between ocean and atmosphere all take place through this surface. This exchange is crucial for the climate system, in which ocean and atmosphere are interlinked. At the same time, the ocean surface is not an immovable shell, but a medium over which waves can travel. These waves ensure that exchange between the ocean and the atmosphere not only takes place in the vertical direction, but also results in a so-called wave-driven transport of, for example, floating particles over the surface of the ocean. This wave-driven transport is one of the reasons that garbage washes up on the beach after a storm.
My research at TU Delft focuses on understanding wave-driven transport, including floating plastic waste. What determines how quickly a floating soda bottle is carried away by a wave and whether this bottle washes up on the beach? During the transport of a plastic particle through the ocean, fluid mechanics processes play a role that span many magnitudes: from gyres (large-scale ocean vortices)
and currents on a scale of hundreds to thousands of kilometers, vortices of tens to hundreds of kilometers, waves and fronts on a scale from tens to hundreds of meters, and turbulent mixing processes on a scale from millimeters to tens of meters. Understanding these processes and predicting the transport of, for example, floating plastic using mathematical models and laboratory experiments is the goal of my research.