Orchestrating Smart Charging Electric Vehicles in mass deployment
Themes: Energy, Software technology & Intelligent Vehicles

A TRL is a measure to indicate the matureness of a developing technology. When an innovative idea is discovered it is often not directly suitable for application. Usually such novel idea is subjected to further experimentation, testing and prototyping before it can be implemented. The image below shows how to read TRL’s to categorise the innovative ideas.
Summary of the project
With Electric Vehicles (EV) becoming more common on the road there is also an increase of charging demand to the current power grid. The most regular way of charging your vehicle is uncontrolled charging, which is to have it start charging once it is connected to a charger so the battery is full when you need the car again. However, the current low voltage distribution grid is not designed to have so many EV’s charging at the same time next to the existing power demand e.g. households or offices.
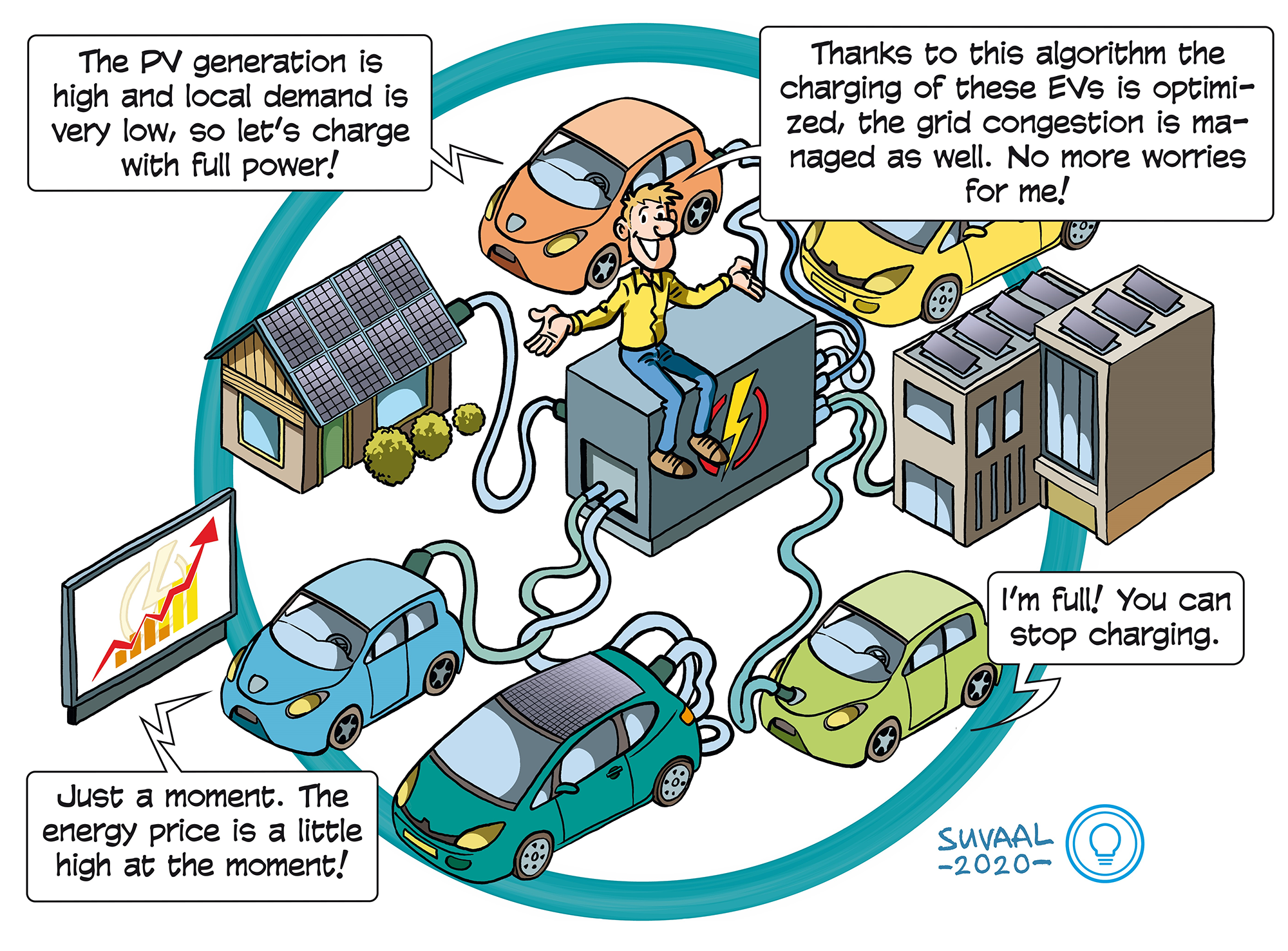
The aim of the research is to build a hierarchical multi-functional algorithm whose job it is to schedule the EV charging smartly. The outcome of this algorithm is to fulfill the charging request process of a large number of Electrical Vehicles while preventing congestion of the grid, reducing the charging cost, increasing the local renewable energy utilization as well as providing grid regulation service. The algorithm will work on two levels. On the local level it will optimize the EV charging process based on the electricity price and the local information e.g. the PV generation, the base load demand and the EV requirements. On the central level the algorithm will coordinate with the local level to match the total demand with the capacity of the whole grid. There are many practical limitations e.g. the communication protocol restriction and the data availability that are not considered in the existing charging scheduling algorithms. The innovative idea of this research is thus to design the algorithm in such a way that it contains multiple functions but also complies with the practical limitations.
What's next?
The next step for the research is to improve the functionality of the algorithm such as to add stochastic optimization and to improve its central coordination functionality so that the algorithm can be better implemented in practical environment. In the meanwhile, we are also verifying and evaluating the algorithm through hardware in the testing simulations in the lab. In the end, an intelligent algorithm will be developed.
Ir. Yunhe Yu
Dr. ir. Gautham Ram Chandra Mouli
Powerweb Institute
Powerweb Institute
Dr.ir. Aditya Shekhar
Prof. dr. Pavol Bauer
Other research partner organizations
-
ElaadNL, Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT), Driivz Ltd., Compleo Charging Solutions gmbh.
This project is funded by Electric Mobility Europe (EME)
Faculties involved
- Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science
