Glass breaks, doesn’t it? It’s wonderfully suited to creating light effects and a sense of spaciousness. But can it be used in a load-bearing capacity, for instance in walls, bridges and pillars? The answer is yes: under pressure glass becomes incredibly tough. TU Delft’s Stevin II laboratory is home to one of the few teams in the world doing research into the suitability of glass as a building material. Here PhDs and professors are finding ways to make glass in construction strong and safe without compromising on transparency.
Cast glass
‘Right, we’ve got our space suits on, let’s open the glass furnace!’ Friends, fellow-Greeks and PhDs Telesilla Bristogianni and Faidra Oikonomopoulou are at the Civil Engineering and Geosciences glass lab, decked out in shiny metallic protective clothing complete with masks and giant gloves. The furnace has been heated to a temperature of 1000 degrees Celsius and Tele and Faidra are ready for the next experiment. They are heating shards of glass placed on top of an earthenware pot. The glass melts and leaks into the pot. Via a hole in the bottom of the pot the molten glass flows evenly into a mould. Then the furnace is left to cool down slowly. This allows the glass to harden in controlled manner so it won’t crack at the centre. The results of previous experiments are strewn around the lab: bricks, lego bricks, pillars and cylinders of cast glass.
Transparent bricks
It all started with the Crystal House in Amsterdam’s P.C. Hooftstraat. Chanel planned to open a flagship store there and wanted a glass façade. But the building is a monument and has to meet certain requirements. One of the requirements is that the façade be made up of bricks of a certain size. The architect’s way around it was to opt for glass bricks. Promotors Fred Veer and ‘glass professor’ Rob Nijsse invited Faidra and Tele to look into the design and manufacturing process of the bricks and the construction of a glass façade to see if it could be done. After all it would have to hold up it’s own weight and the windload.
The challenge was to make the bricks and the structure itself strong, vandal proof and as transparent as possible. ‘We had to think of lots of ways of testing this,’ Faidra explains. ‘How do you determine the strength of a glass brick or wall? How do we make the bricks and how do we cool them down in a way that keeps them transparent? And what do we use to stick them together?’ Cement was out because it would compromise transparency. Still, they had to find something to turn the separate bricks into a strong monolithic structure. The solution they hit upon was a transparent glue which can withstand the changes in temperatures a structure like this is subject to.
Vandal proof
Once the experimental glass wall was up it could be tested. In order to determine its strength Faidra was allowed to release her inner vandal and hit it as hard as she could using a hammer. While some of the bricks shattered the structure itself remained intact. The building of the façade could begin. Faidra and Tele singlehandedly built the first 1.5 meters of the façade. ‘We were laying bricks at the construction site from 7.30 in the morning to 7.30 at night to show the workmen how it was done,’ says Tele. ‘It was tough but a good way of learning to manage a big project.’
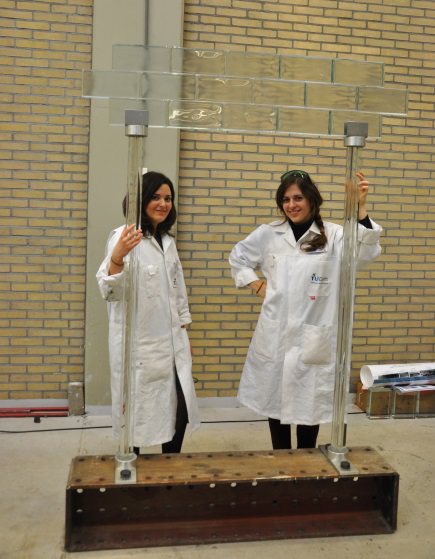
Glass columns
Back at the lab the research group is building on the new ideas generated by the Crystal House project. Faidra and Tele are studying the manufacture of glass columns. Pillars or columns made of concrete break up a space and obstruct the view, which makes them the pet hatred of many architects. They are a necessary evil, however, because they carry the weight of a roof or ceiling. But could glass be used instead?
‘People are not completely convinced that glass is actually strong enough,’. Tele says. ‘We can show them the scientific proof of course but there’s a psychological aspect to consider as well. A ceiling that rests on two transparent pillars that are barely visible can freak people out: that ceiling isn’t held up by anything!’ That is why the duo is making the columns slightly less transparent than the bricks used for the Crystal House. Faidra developed a new version of the bundles column, consisting of 7 transparent glass rods that are joined and glued together. This causes the light in the rods to refract making the pillars easy to distinguish. ‘And it has the added bonus of preventing people from bumping into them.’
What next? The two girls would love to replace one of the pillars of the Berlagezaal with a glass one. ‘Then visitors would no longer mind being stuck behind a pillar!’ One of their other main ambitions is the project ‘Restoration by Glass’. Here they want to restore historic damaged monuments by replacing the missing components with glass. But for the remains of this day, all that’s left to do is to make sure the oven is set correctly to slowly cool down the glass component inside. Time to take off the extremely warm masks.
Published: September 2016