Latest News
26 August 2022
New CRISPR-Cas system with on-off switch cuts proteins
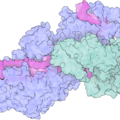
Researchers from TU Delft in the group of Stan Broun have discovered a CRISPR-Cas system that cuts proteins instead of DNA.
25 August 2022
Cells: strong at the right place and time
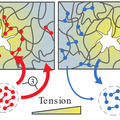
Researchers from TU Delft and NWO institute AMOLF discovered how certain molecular bonds make living cells both flexible, in order to move, as well as strong, in order to withstand forces.
04 August 2022
TU Delft researchers create flow-driven rotors at the nanoscale
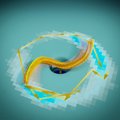
Onderzoekers van de TU Delft hebben de kleinste door stroming gedreven motoren ter wereld ontwikkeld. Geïnspireerd door de iconische Nederlandse windmolens en door biologische motoreiwitten hebben ze een zichzelf configurerende, stromingsgedreven turbine uit DNA gemaakt, die energie van een elektrische of zoutgradiënt omzet in bruikbaar mechanisch vermogen. De resultaten bieden perspectief voor de ontwikkeling van actieve robotica op nanoschaal. Het artikel is vandaag gepubliceerd in Nature Physics.
08 July 2022
Evolutionary model predicts how cells control the partitioning of their molecules
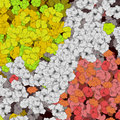
Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organisation in Göttingen, Germany, and the TU Delft in the Netherlands have developed a new method to study how mixtures, consisting of many different molecules, interact to reliable form different droplets, as happens continuously in the living cell. This is the first time that scientists designed a model of many interacting molecules that can predict how particular droplets form. They published their findings in PNAS this week.
14 April 2022
Rubicon grant for Jochem Vink

Jochem Vink (Bionanoscience) has received a Rubicon grant from NWO, which enables him to gain research experience at a leading institute abroad. His research will be about useful fungi attracting pathogens. He was awarded the coveted grant along with 21 other researchers who recently received their PhDs.
16 March 2022
New Cas9 model maps DNA cutting behaviour for the first time
Researchers from the TU Delft have come up with a physical-based model that establishes a quantitative framework on how gene-editing with CRISPR-Cas9 works, and allows them to predict where, with what probability, and why targeting errors (off-targets) occur. This research, which has been published in Nature Communications, gives us a first detailed physical understanding of the mechanism behind the most important gene editing platform of today.
14 March 2022
IM Claire Wyman
With deep regret we announce the passing away of Prof.dr. Claire Wyman, founder and long-term director of the Nanobiology programme, on Thursday March 10. Claire has been ill for some time. Her passing affects us immensely.
23 February 2022
Signal discovered that connects cell size with cell growth
The mechanisms connecting growth with cell size have been mysterious – up till now: in a recent publication in Current Biology, researchers from TU Delft and AMOLF have uncovered that the signaling molecule ppGpp is essential to regulate cell size. Surprisingly, they also discover cells adjust their sizes to concentrations of ppGpp, rather than strictly according to growth rate.
07 February 2022
ERC Proof of Concept Grant for Arjen Jakobi

Arjen Jakobi (Department of Bionanoscience) receives the ERC Proof of Concept Grant for his groundbreaking research on cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM). "This grant will allow us to take our new CryoChip technique for high resolution images of protein molecules to the next level for the development of new drugs," says Jakobi.
31 January 2022
The Boukany and the Koenderink groups have been awarded an EMW-M-2 grant (700 kEuro)
Genome editing technologies such as CRISPR-Cas systems are revolutionizing the life sciences because they make it possible to change or repair the genomes of cells with high precision. However, a major challenge that hampers widespread application is that genome editing requires getting molecular tools (nucleic acids and enzymes) into the cell, across the its insulating membrane.