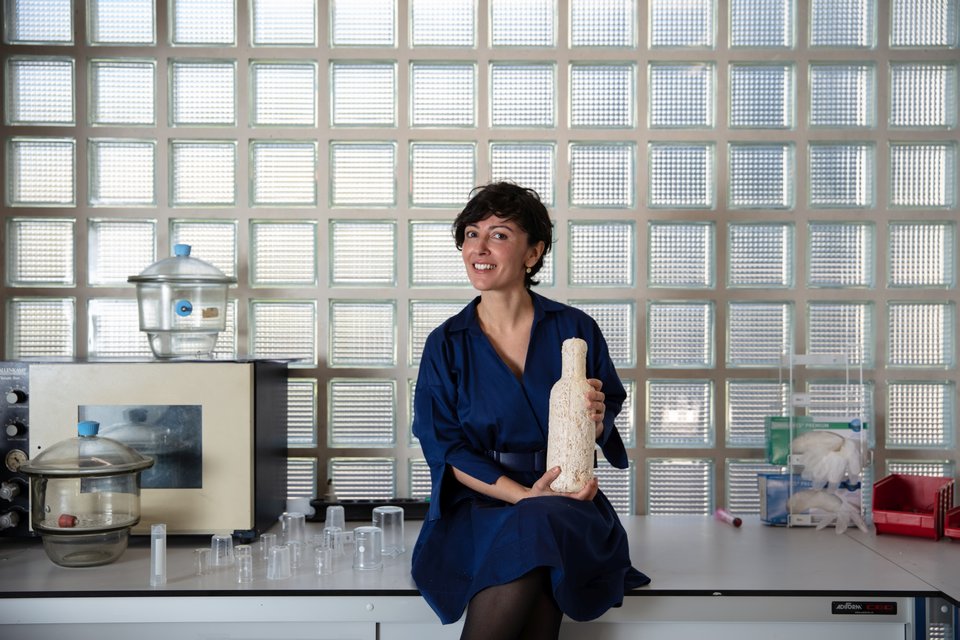
In a circular economy, design is about more than just creating a sustainable product. In this system based on eliminating waste and minimising the use of resources, the design process is aimed at preserving the value of products and materials and keeping them in the economic system for as long as possible. So how do you do that? PhD candidate Marita Sauerwein came up with a novel material based on ground mussel shells and showed through 3D printing technology that the end life of a product is really just the beginning.
Header photo product design: Edwin van Tongeren
Inspired by waste
In the early stages of her PhD, Sauerwein interviewed designers that 3D printed with sustainability in mind. She found that the materials being used did not support the aim of maintaining product or material integrity or the value of post-product from materials. That prompted her to explore materials that would be renewable, from bio-based sources, but that would also fit in the circular economy. And though mussel shells are not the only material that meet the goals of a circular system, they are a huge waste stream in the Netherlands due to large-scale mussel processing plants. So, this plentiful and local source was a logical and appropriate place to begin.
It’s all about the binding agent
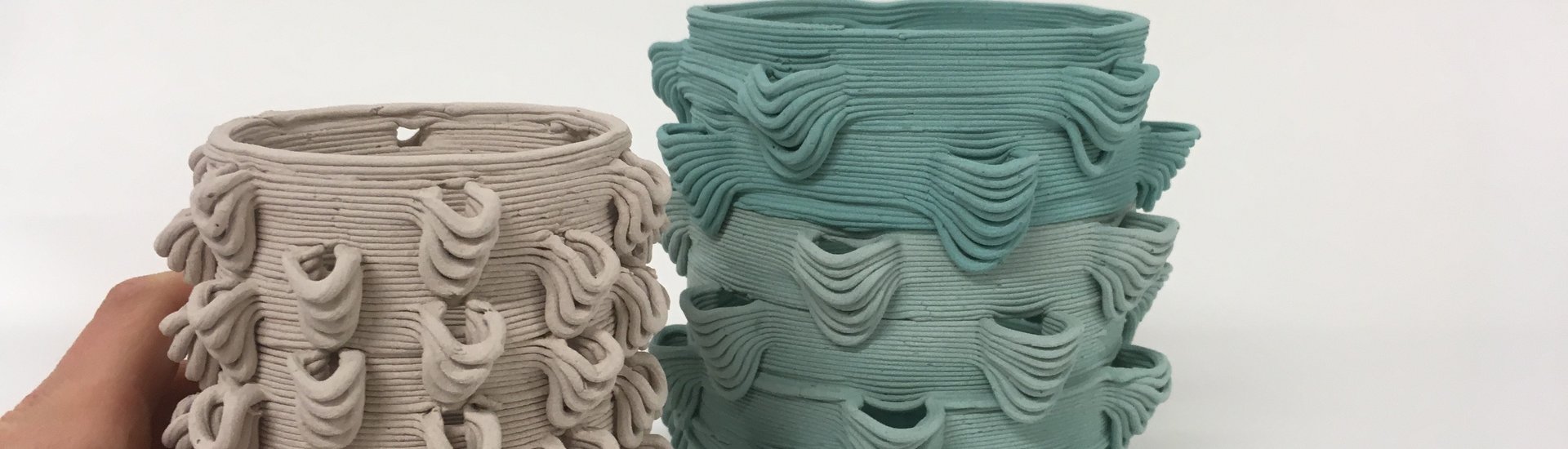
To create a material suitable for 3D printing, Sauerwein says the most important factor next to the mussel shells is the binding agent. To make a composite material, the ground up shells have to be bound by something. And it’s this binding substance that influences how to reuse the material and whether it fits within the circular economy philosophy. “What I wanted to achieve is that it’s not only compostable, but reusable on a higher level,” she said. In addition to being reusable, she also wanted to create a material that is re-printable.
Initially the research involved using sugar water to bond the mussel shells. After drying, it becomes a ceramic-like hard material. Sauerwein was able to produce a 3D printed lampshade using this material. In this example, when the object becomes obsolete you can add water, causing the material to dissolve back into a paste, which can be used to 3D print again. But the fact that it’s not water resistant also limits its use.
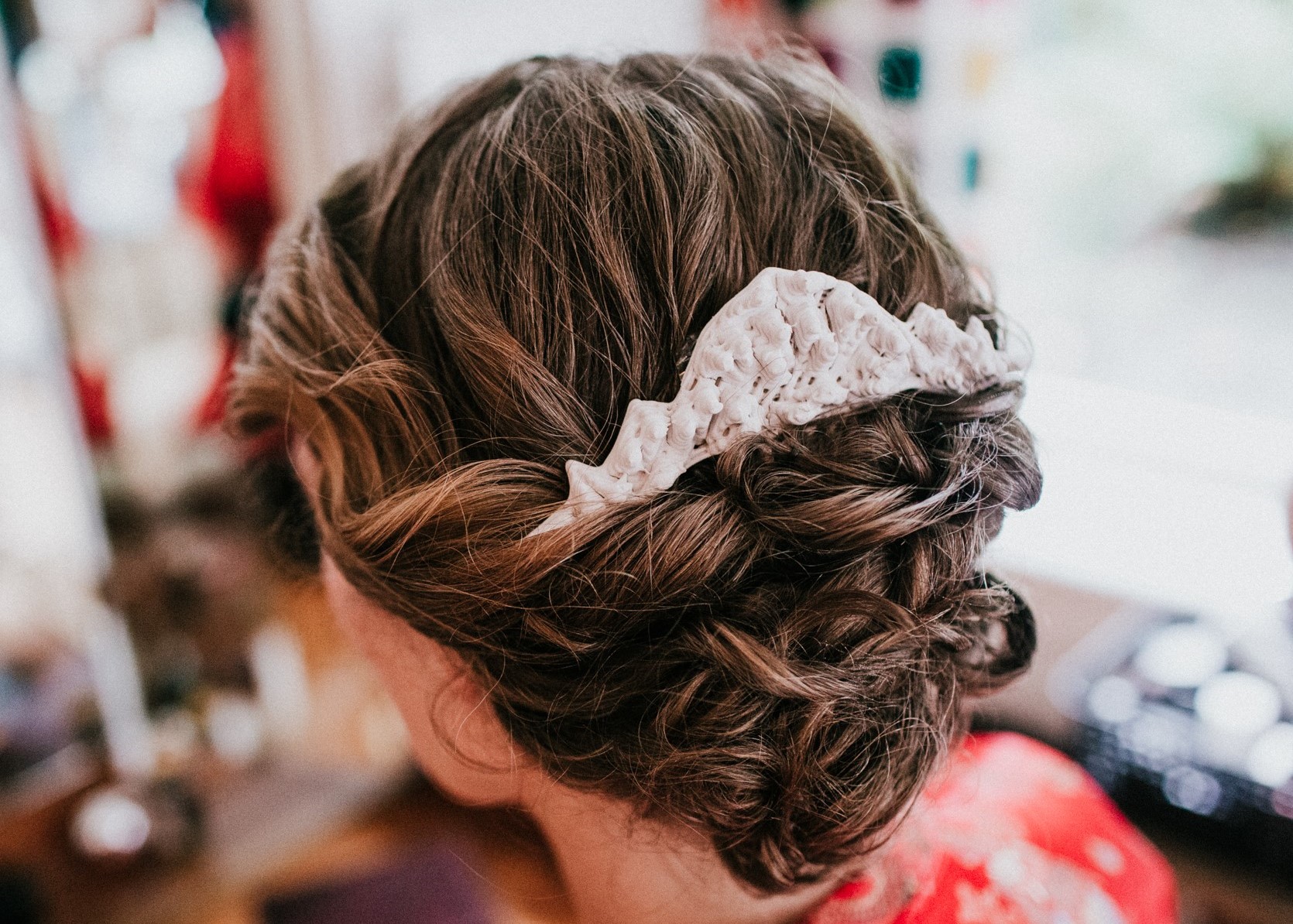
With some help from a biopolymer lab at the Applied Sciences faculty of TU Delft, Sauerwein learned that alginate could be used to create a water-resistant material through ion cross-linking. This reaction can then be reversed, producing a printable paste once again. With this material, she 3D printed a flat hair accessory that when made wet again could be bent or shaped to fit the curve of the head. “It’s a very good example of what is possible with this material,” she said.
A new spin on methodology
Sauerwein chose to use a Research through Design (RtD) methodology because she wanted to make the findings more concrete. But she took a slightly different approach than is commonly used. She explained that often a product is designed and then tests are done with that product or prototype to continue generating knowledge and insights. “In my case the prototype is kind of the proof of concept, the end product,” she said. “The lampshade shows that there’s this new material that can be reprinted and that you can actually make another product with it.”
In the future, Sauerwein hopes to see more focus on the use of biobased materials but says that is not enough to make a sustainable or circular economy. “You should also think about the end of life, how it can be recovered and reused at the highest level possible. In the initial design process, you have to think about reuse. You don’t have to entirely know how something will be reused, but you have to make sure that you enable this.”

Zjenja Doubrovski
- +31 (0)15 278 63 67
- e.l.doubrovski@tudelft.nl
-
Room B-3-030
Conny Bakker
- +31 (0)15 27 89822
- C.A.Bakker@tudelft.nl
-
Room B-3-330

Ruud Balkenende
- +31 15 27 81658
- a.r.balkenende@tudelft.nl
-
Room B-3-310