Power module design in solid state transformers
Project description
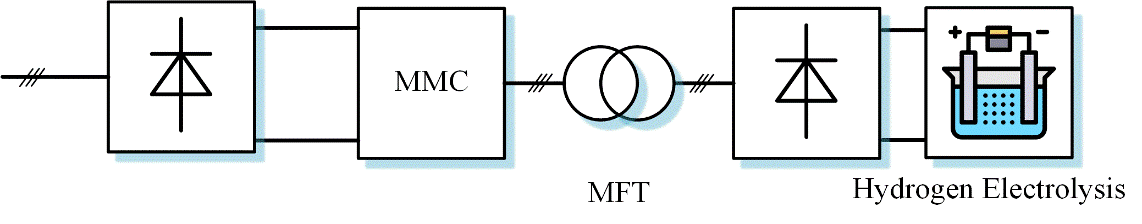
PtG is of particular interest because of its potential to provide flexibility to the energy system and hence contribute to the implementation of intermittent energy sources. The current industrial practice of power conversion for hydrogen production is utilizing a line frequency step-down transformer and an AC-DC rectifier using diode or thyristor. This current practice is mainly facing two bottlenecks. One is that it is bulky and heavy, and the other is the lack of controllability.
To break the bottlenecks and reduce the LCOH, the promising technology, solid state transformer (SST), can be applied to replace the line frequency transformer. The fundamental idea of SST is to use power electronics technology to convert the line frequency (50 Hz) medium AC voltage into medium/high frequency (e.g. 400Hz) AC voltage, then a medium/high frequency transformer can be used to step down the voltage. Generally, the transformer’s weight and volume are inversely proportional to its operation frequency, so there is still a huge potential to reduce the weight, volume, and requirement of magnetic material using SST. This research focuses on the power electronics converter design and modelling.
The research questions associated with this PhD project are as follows:
1. What are the most suitable topology, power switch, and modulation strategy for the SST?
2. How to design the control strategies in normal conditions, abnormal conditions, optimal operation control of electrolyser, and local protection strategy?
3. How to analyse the stability issue of SST, considering numerous numbers of MMC modules, which increase complexity of impedance modelling compared with simple three phase or single phase inverter?
PhD Candidate
Zhengzhao Li, Z.Li-20@tudelft.nl
Supervisor
Zian Qin, Z.Qin-2@tudelft.nl
Promotor
Prof. dr. Pavol Bauer, P.Bauer@tudelft.nl